基于MobileNetV3架构动物声音分类识别与应用系统实现
1.摘要
本文主要实现了一个基于MobileNetV3架构的深度学习模型用于动物声音分类识别任务。该MobileNetV3是一种轻量级的卷积神经网络,旨在实现高效分类性能,本章在猫、狗、海豚等三个动物声音(.wav数据集)上进行了训练和测试,即在动物音频数据集上进行训练,以学习区分不同动物的声音特征,其准确率可达92%。最后本文基于训练好的模型参数实现了一个动物声音分类识别的网页系统,该系统功能功能包含上传音频进行识别和录音识别。
2.MobileNetV3模型设计与实现
代码实现细节:
使用PyTorch框架实现模型,包括定义各种网络层、激活函数、倒置残差块等组件。
通过_make_divisible函数确保所有层的通道数都是8的倍数,这有助于在硬件上实现更高效的计算。
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
class h_sigmoid(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_sigmoid, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return self.relu(x + 3) / 6
class h_swish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_swish, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid = h_sigmoid(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.sigmoid(x)
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=4):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, _make_divisible(channel // reduction, 8)),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(_make_divisible(channel // reduction, 8), channel),
h_sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
def conv_3x3_bn(inp, oup, stride):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
h_swish()
)
def conv_1x1_bn(inp, oup):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
h_swish()
)
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, hidden_dim, oup, kernel_size, stride, use_se, use_hs):
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
assert stride in [1, 2]
self.identity = stride == 1 and inp == oup
if inp == hidden_dim:
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
# dw
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, stride, (kernel_size - 1) // 2, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
h_swish() if use_hs else nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# Squeeze-and-Excite
SELayer(hidden_dim) if use_se else nn.Identity(),
# pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
else:
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
# pw
nn.Conv2d(inp, hidden_dim, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
h_swish() if use_hs else nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# dw
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, stride, (kernel_size - 1) // 2, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
# Squeeze-and-Excite
SELayer(hidden_dim) if use_se else nn.Identity(),
h_swish() if use_hs else nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
def forward(self, x):
if self.identity:
return x + self.conv(x)
else:
return self.conv(x)
class MobileNetV3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfgs, mode, num_classes=1000, width_mult=1.):
super(MobileNetV3, self).__init__()
# setting of inverted residual blocks
self.cfgs = cfgs
assert mode in ['large', 'small']
# building first layer
input_channel = _make_divisible(16 * width_mult, 8)
layers = [conv_3x3_bn(3, input_channel, 2)]
# building inverted residual blocks
block = InvertedResidual
for k, t, c, use_se, use_hs, s in self.cfgs:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width_mult, 8)
exp_size = _make_divisible(input_channel * t, 8)
layers.append(block(input_channel, exp_size, output_channel, k, s, use_se, use_hs))
input_channel = output_channel
self.features = nn.Sequential(*layers)
# building last several layers
self.conv = conv_1x1_bn(input_channel, exp_size)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
output_channel = {'large': 1280, 'small': 1024}
output_channel = _make_divisible(output_channel[mode] * width_mult, 8) if width_mult > 1.0 else output_channel[mode]
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(exp_size, output_channel),
h_swish(),
nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(output_channel, num_classes),
)
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
n = m.weight.size(1)
m.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
m.bias.data.zero_()
MobileNetV3 模型的设计思路主要集中在构建高效、轻量级的神经网络架构,以适应移动和嵌入式设备上的计算资源限制。其设计思路如下:
1.使用深度可分离卷积(Depthwise Separable Convolutions)来减少计算量和模型参数,这是MobileNet系列的核心技术。引入新的激活函数h-swish,它是基于swish函数的改进版本,旨在减少计算复杂度的同时保持模型性能。
2.网络结构创新:
采用倒置残差块(Inverted Residual Block)作为模型的主要构建单元,这种结构通过先扩展通道数进行深度卷积,再缩小通道数进行逐点卷积的方式,提高了模型的表示能力。
在倒置残差块中集成了SE(Squeeze-and-Excitation)通道注意力机制,通过显式地建模通道间的相关性来增强模型的特征表达能力。
模型宽度和输入尺寸调整:提供了模型宽度的调节参数,允许用户通过调整宽度乘数(width multiplier)来控制模型的复杂性和性能。允许使用不同的输入图像尺寸,以适应不同应用场景的需求。
数据集形式展示如下:
使用如下代码:
def read_file(path):
"""Read wav file"""
wav, _ = librosa.core.load(path, sr=config['sampling_rate'])
wav, _ = librosa.effects.trim(wav)
return wav
def read_wav_files(path):
"""Read all wav files from directory"""
logger.debug("Reading files from %s", path)
features = []
for filename in os.listdir(path):
if filename.endswith(".wav"):
wav = read_file(os.path.join(path, filename))
features.append(wav)
logger.debug("Read %s files", len(features))
return features
def get_mel(wav):
"""Calculate melspectrogram"""
melspec = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(
wav,
sr=config['sampling_rate'],
n_fft=1024,
hop_length=256,
n_mels=128
)
logmel = librosa.core.power_to_db(melspec)
return logmel
read_file(path):使用librosa库读取.wav文件,并修剪静音部分。read_wav_files(path):遍历给定目录中的所有.wav文件,并使用read_file函数读取它们。get_mel(wav):计算给定音频数据的梅尔频谱图(Melspectrogram),这是音频处理中常用的特征提取方法。使用到的核心库函数:
librosa:一个专门用于音频分析的库,有助于执行诸如从声音文件中提取特征等任务。3.系统实现
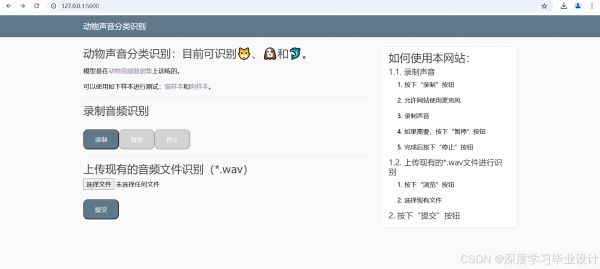
该项目通过构建网页界面和训练好的上述模型,实现了一个动物声音分类识别的系统,为用户提供了一个方便的平台来测试和体验声音识别技术。实现的界面如下:
上传一个声音:
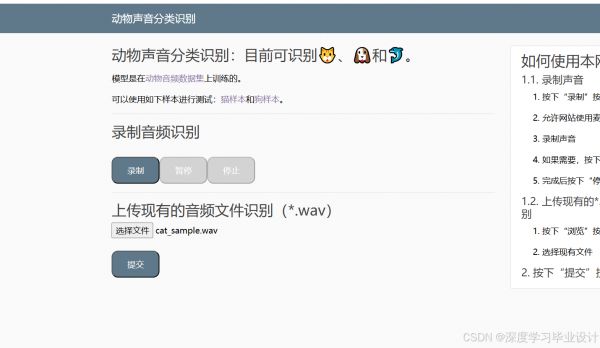
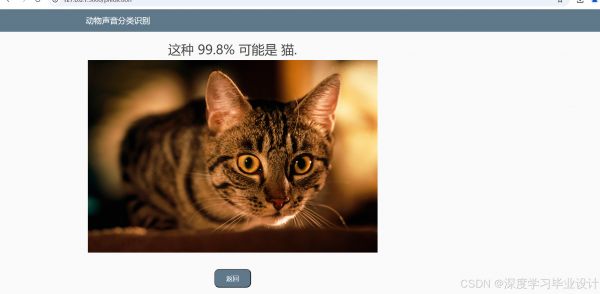
点击提交:
完整代码及数据集:
https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_40651515/90111565https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_40651515/90111565数据集太大加qq找我索要。
相关知识
基于MobileNetV3架构动物声音分类识别与应用系统实现
基于卷积神经网络通过声音识别动物情绪的方法及系统
深度学习之基于Tensorflow卷积神经网络(CNN)动物识别分类系统
基于卷积神经网络通过声音识别动物情绪的方法及系统与流程
动物声音识别
基于深度学习的鸟类声音识别系统
使用PyTorch进行城市声音分类:PyTorch音频识别
使用GitCode上的Audioset Tagging CNN进行音频识别与分类
基于Pytorch实现的声音分类
基于Python深度学习的【猫狗宠物识别】系统设计实现
网址: 基于MobileNetV3架构动物声音分类识别与应用系统实现 https://www.mcbbbk.com/newsview1073081.html
| 上一篇: 玄凤鹦鹉怎么分辨雌雄?教你几招轻 |
下一篇: 一种基于神经网络的宠物声音识别方 |
推荐分享

- 1养玉米蛇的危害 28694
- 2狗交配为什么会锁住?从狗狗生 7180
- 3我的狗老公李淑敏33——如何 6236
- 4豆柴犬为什么不建议养?可爱的 4637
- 5南京宠物粮食薄荷饼宠物食品包 4563
- 6中国境内禁养的十大鸟种,你知 4429
- 7湖南隆飞尔动物药业有限公司宠 4259
- 8自制狗狗辅食:棉花面纱犬的美 4257
- 9家养水獭多少钱一只正常 4212
- 10广州哪里卖宠物猫狗的选择性多 4122






