生物多样性背景下城市动物生境营建的策略与方法
摘要:
目的
当前城市化进程的加快对于生物多样性提出了严峻考验,梳理动物生境营建的策略与方法,可为城市生物多样性和绿地生态服务功能提升提供借鉴。
方法
通过综述国内外城市动物生境研究现状,以城市生物多样性保护和提升为导向,探讨动物的生境偏好特征,总结城市动物生境营建的策略和方法。
结果
提出了“要素调查—营建内容—生境管理”的城市动物生境营建基本内容。1)要素调查:以鸟类、小型哺乳类和两栖类动物作为目标类群,调查物种资源和生境资源以明确生态本底信息,并根据动物的生境偏好分析,总结食源地、水源地和庇护地的环境特征。2)营建内容:从植被营建、水体营造和设施构建3个方面,提出城市动物生境的营建方法。3)生境管理:指出持续开展生态监测与游憩管理,有助于设计者或管理者更好地改进优化动物生境。
结论
上述基本内容可为城市生物多样性保护和提升提供理论支撑,也可作为风景园林与生态实践相结合的重要指导依据。对于城市动物栖息环境的优化建设、城市绿色空间生态功能的发挥和可持续发展具有重要意义,具有理论借鉴及规划参考的双重价值。
Abstract:
Objective
In recent years, the rapid development of urbanization has had a significant impact on the ecological environment of cities and the survival of animals living in cities, causing a serious challenge to urban biodiversity. Based on combing the strategies and methods of animal habitat construction, it aims to restore or construct suitable animal habitats to protect and enhance urban biodiversity, which is a theoretical research hotspot that is widely concerned by the academic community.
Method
In view of the protection and enhancement of urban biodiversity, this research reviews the current status of researches on urban animal habitat at home and abroad through literature analysis, and systematically sorts out the researches on animal habitat preferences and habitat environment restoration and improvement. Based on the progress of scientific research and related landscape practice, the research summarizes the strategies and methods for urban animal habitat construction.
Results
The research proposes basic contents for urban animal habitat construction, which are composed of “factor investigation-construction content-habitat management”. 1) Factor investigation includes understanding ecological background information and analyzing habitat preference characteristics. There are many types and quantities of animals in the urban environment, and it is necessary to screen out key species of birds, small mammals and amphibians to improve research efficiency. Through such means as field survey, website data collation, interview survey and map review, the research collects a large amount of data on the type, quantity, distribution and activity rhythm of existing animal species and local ecological base in an effort to grasp the situation of animal resources and site environment in the research area. Based on the analysis of animal habitat preferences, the environmental characteristics of food sources, water sources and shelters to provide a basis for the content of animal habitat construction. 2) In terms of construction content, the construction methods for urban animal habitats are proposed from the three aspects of vegetation construction, water body construction and facility construction. Vegetation construction includes plant species, vegetation structure and community configuration. Native plants are preferentially selected as dominant species to ensure high adaptability and stability of the plant community. The strategy adopted pays attention to the matching of diverse food source tree species and the application of tall nesting tree species with complex branch structures, which can provide abundant food sources and safe shelter spaces for animals to inhabit. The multi-layered vegetation configuration (including arbor layer, shrub layer, herbaceous layer and aquatic plant layer) with complex structure and diverse micro-environments can meet the habitat needs of various animals. It is also necessary to adapt measures to local conditions according to site conditions, and make full use of existing resources such as terrain, water system, and vegetation to ensure diverse, healthy and stable plant community configuration. The construction of water body mainly involves the type of water area, hydraulic engineering practice and island in the water. Creating a water environment with multiple water levels and enrich the type of water area can provide various ecological niches for animals and increase the possibilities for animals to communicate with the surrounding environment. The properties of water body area, water body revetment, water body base and water body edge have great influence on the quality of animal habitat. For excessively large water areas, it is advisable to build islands in water in the open water body to provide a foothold for water birds, and at the same time effectively block the interference of human activities on birds and attract wetland birds to inhabit and breed. Facility construction involves artificial facilities and natural facilities. The artificial auxiliary facilities such as artificial nest boxes, Benjeshecke, insect hotels and fences should be used to attract animals, and natural facilities such as dead woods, fallen trees, fallen leaves and stone piles should be used to help animals avoid natural enemies and reduce the impact of unfavorable environmental conditions. 3) In terms of habitat management, the research conducts continuous ecological monitoring and recreational management to help designers or managers improve and optimize animal habitats. Specifically, the research conducts vegetation monitoring, hydrological monitoring, noise monitoring, and animal diversity monitoring to help determine if a habitat is achieving its goals, identify problems, and take measures for improvement based on monitoring results to better serve relevant user groups. By regulating recreational behaviors, and setting reasonable recreational paths and stations, the research aims to maximize the harmony between human and animals.
Conclusion
This research provides theoretical support for the protection and enhancement of urban biodiversity, and serves as an important guiding principle for the integration of landscape architecture and ecological practice. Therefore, it has dual values for theoretical reference and planning. The research is of great significance for the optimization of animal habitats in urban environments, the ecological functions of urban green spaces, and sustainable development. However, in the future, further research is still needed on different types of green spaces, ecological relationships between different animal groups, and comprehensive allocation of green space resources.
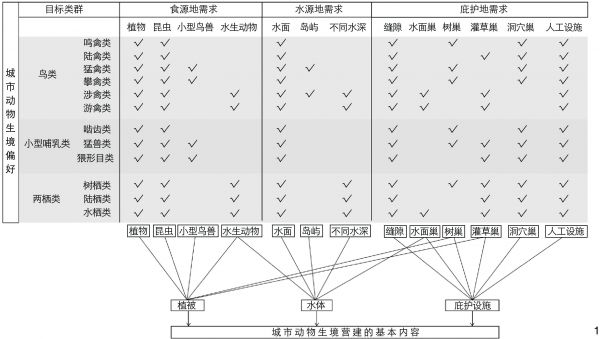
图 1 动物生境偏好与主要生境因子
Figure 1. Animal habitat preference and main habitat factors

图 2 人工设施示意
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of artificial facilities

图 3 天然设施示意
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of natural facilities
[1] 徐炜,马志远,井新,等.生物多样性与生态系统多功能性:进展与展望[J].生物多样性,2016,24(1):55-71. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015091XU W,MA Z Y,JING X,et al. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Multifunctionality: Advances and Perspectives[J]. Biodiversity Science,2016,24 (1): 55-71. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015091
[2]ANDREN H. Effects of Habitat Fragmentation on Birds and Mammals in Landscapes with Different Proportions of Suitable Habitat: A Review[J]. Oikos,1994,71 (3): 355-366. doi: 10.2307/3545823
[3]BROWN M L,DONOVAN T M,SCHWENK W S,et al. Predicting Impacts of Future Human Population Growth and Development on Occupancy Rates of Forest-Dependent Birds[J]. Biological Conservation,2014,170: 311-320. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2013.07.039
[4]MASEKO M S T,RAMESH T,KALLE R,et al. Response of Crested Guinea-Fowl (Guttera edouardi),a Forest Specialist,to Spatial Variation in Land Use in iSimangaliso Wetland Park,South Africa[J]. Journal of Ornithology,2017,158 (2): 469-477. doi: 10.1007/s10336-016-1406-7
[5]MASEKO M S T,ZUNGU M M,SMITH D A E,et al. High Microhabitat Heterogeneity Drives High Functional Traits in Forest Birds in Five Protected Forest Areas in the Urban Mosaic of Durban,South Africa[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation,2019,18: e00645. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00645
[6]MORRISON M L, MARCOT B G, MANNAN R W. Wildlife-Habitat Relationships: Concepts and Applications[M]. Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin Press, 1992.
[7] 史娜娜,郭宁宁,刘高慧,等.北京市两栖爬行动物空间分布格局及影响因素[J].生态学报,2022,42(9):3806-3821.SHI N N,GUO N N,LIU G H,et al. Spatial Distribution Pattern and Influencing Factors of Amphibians and Reptiles in Beijing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022,42 (9): 3806-3821.
[8] 干靓,郭光普.基于生态位需求的高密度城区鸟类微生境选择研究:以上海市浦东新区世纪大道地区为例[J].风景园林,2017,24(11):86-92.GAN L,GUO G P. Microhabitat Selection for Wild Birds in High-density Urban Areas Based on Niche Demand: Case Study in Century Avenue Area,Pudong New District,Shanghai[J]. Landscape Architecture,2017,24 (11): 86-92.
[9]OSMAN A,MARIWAH S,YAWSON D O,et al. Changing Land Cover and Small Mammal Habitats: Implications for Landscape Ecological Integrity[J]. Environmental Challenges,2022,7: 100514. doi: 10.1016/j.envc.2022.100514
[10]DE GROEVE J,CAGNACCI F,RANC N,et al. Individual Movement-Sequence Analysis Method (IM-SAM): Characterizing Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Animal Habitat Use Across Landscapes[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science,2020,34 (8): 1530-1551. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2019.1594822
[11] 张颖,黄婷婷,胡骞,等.基于鸟类多样性提升的社区公园生境营造策略探析[J].中国园林,2022,38(3):106-111.ZHANG Y,HUANG T T,HU Q,et al. Analysis on the Habitat Design Strategy of Community Park Based on the Improvement of Bird Diversity[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2022,38 (3): 106-111.
[12] 李晖,刘彦,黄伊琳,等.基于Maxent模型的深圳湾鸟类热点生境判别及修复研究[J].中国园林,2022,38(12):14-19.LI H,LIU Y,HUANG Y L,et al. Study on the Identification and Restoration of Bird Hotspot Habitats in Shenzhen Bay Based on Maxent Model[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2022,38 (12): 14-19.
[13] 刘海龙,王茜,宋洋,等.北京第二绿化隔离地区以鸟类为主的城市生物多样性保护规划途径[J].中国园林,2022,38(10):6-13.LIU H L,WANG Q,SONG Y,et al. The Planning Approach for Bird-Based Urban Biodiversity Conservation in the Second Green Belt of Beijing[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2022,38 (10): 6-13.
[14] 陈梦芸,林广思.城市中心区湿地生物多样性提升策略研究:以海珠湿地为例[J].中国园林,2022,38(10):20-25.CHEN M Y,LIN G S. Biodiversity Enhancement Strategies for Urban Wetlands: A Case Study of Haizhu National Wetland Park[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2022,38 (10): 20-25.
[15]GOMES V,RIBEIRO R,CARRETERO M A. Effects of Urban Habitat Fragmentation on Common Small Mammals: Species Versus Communities[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation,2011,20 (14): 3577-3590. doi: 10.1007/s10531-011-0149-2
[16] 李成,谢锋,车静,等.中国关键地区两栖爬行动物多样性监测与研究[J].生物多样性,2017,25(3):246-254. doi: 10.17520/biods.2016137LI C,XIE F,CHE J,et al. Monitoring and Research of Amphibians and Reptiles Diversity in Key Areas of China[J]. Biodiversity Science,2017,25 (3): 246-254. doi: 10.17520/biods.2016137
[17]ARMSTRONG D,CARO T. Focal and Surrogate Species: Getting the Language Right[J]. Conservation Biology,2002,16 (2): 285-287.
[18] 俞孔坚,李迪华,段铁武.生物多样性保护的景观规划途径[J].生物多样性,1998,6(3):45-52.YU K J,Li D H,DUN T W. Landscape Approaches in Biodiversity Convention[J]. Chinese Biodiversity,1998,6 (3): 45-52.
[19] 胡望舒,王思思,李迪华.基于焦点物种的北京市生物保护安全格局规划[J].生态学报,2010,30(16):4266-4276.HU W S,WANG S S,LI D H. Biological Conservation Security Patterns Plan in Beijing Based on the Focal Species Approach[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2010,30 (16): 4266-4276.
[20] 邱玲.生态单元制图在城乡生物多样性保护中的研究[J].南方建筑,2016,36(4):47-49.QIU L. Study of Biotope Mapping in Urban Biodiversity Conservation[J]. South Architecture,2016,36 (4): 47-49.
[21] 张颖,朱建宁.融入风景园林因子的生境单元制图法及在公园鸟类微生境研究中的应用[J].风景园林,2021,28(2):96-102.ZHANG Y,ZHU J N. Biotope Mapping with Landscape Architecture Elements and lts Application in the Research of Park Avian Microhabitats[J]. Landscape Architecture,2021,28 (2): 96-102.
[22] 陈天一,赵聪聪,文素洁,等.城市生境单元制图研究进展及其在生物多样性保护中的应用[J].风景园林,2022,29(1):12-17.CHEN T Y,ZHAO C C,WEN S J,et al. Research Progress in Urban Biotope Mapping and Its Application in Biodiversity Conservation[J]. Landscape Architecture,2022,29 (1): 12-17.
[23]FRĄCKOWIAK W,THEUERKAUF J,PIRGA B,et al. Brown Bear Habitat Selection in Relation to Anthropogenic Structures in the Bieszczady Mountains,Poland[J]. Biologia (Bratisl),2014,69 (7): 926-930. doi: 10.2478/s11756-014-0386-4
[24]WANG J,JI S N,WU J Y,et al. Away from the City: Habitat Selection of Badgers in Mountainous Area Around Beijing[J]. Biologia (Bratisl),2021,76 (6): 1-10.
[25]BURON R,HOSTETLER M E,ANDREU M. Urban Forest Fragments vs Residential Neighborhoods: Urban Habitat Preference of Migratory Birds[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning,2022,227: 104538. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2022.104538
[26]KOBRYN H T,SWINHOE E J,BATEMAN P W,et al. Foxes at Your Front Door? Habitat Selection and Home Range Estimation of Suburban Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes)[J]. Urban Ecosystems,2022,26 (1): 1-17.
[27]SZAŁKIEWICZ E,KAŁUŻA T,GRYGORUK M. Detailed Analysis of Habitat Suitability Curves for Macroinvertebrates and Functional Feeding Groups[J]. Scientific Reports,2022,12 (1): 10757. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15096-8
[28] 王成,刘红玉,李玉凤,等.盐城滨海湿地水鸟类群生境适宜性及生态阈值研究:对栖息地景观结构恢复的启示[J].生态与农村环境学报,2022,38(7):897-908.WANG C,LIU H Y,LI Y F,et al. A Study on Habitat Suitability and Ecological Threshold of Waterbird Guilds in Yancheng Coastal Wetlands: Implications for Habitat Structure Restoration[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2022,38 (7): 897-908.
[29]PARDEE G L,PHILPOTT S M. Native Plants Are the Bee’s Knees: Local and Landscape Predictors of Bee Richness and Abundance in Backyard Gardens[J]. Urban Ecosystems,2014,17 (3): 641-659. doi: 10.1007/s11252-014-0349-0
[30]SNEP R P H,KOOIJMANS J L,KWAK R G M,et al. Urban Bird Conservation: Presenting Stakeholder-Specific Arguments for the Development of Bird-Friendly Cities[J]. Urban Ecosystems,2016,19 (4): 1535-1550. doi: 10.1007/s11252-015-0442-z
[31]BURGHARDT K T,TALLAMY D W,GREGORY SHRIVER W. Impact of Native Plants on Bird and Butterfly Biodiversity in Suburban Landscapes[J]. Conservation Biology,2009,23 (1): 219-224. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2008.01076.x
[32]SALISBURY A,ARMITAGE J,BOSTOCK H,et al. Editor’s Choice: Enhancing Gardens as Habitats for Flower-Visiting Aerial Insects (Pollinators): Should We Plant Native or Exotic Species?[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology,2015,52 (5): 1156-1164. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.12499
[33] 张庆费.野生动物友好型绿地的设计理念与思路[J].园林,2015,32(1):12-16.ZHANG Q F. The Design Concept and Thinking of Wildlife-Friendly Green Space[J]. Landscape Architecture Academic Journal,2015,32 (1): 12-16.
[34] 朱光,王雪,张文文,等.城市景观格局对鸟类群落的影响:以南京溧水区为例[J].生态与农村环境学报,2022,38(3):327-333.ZHU G,WANG X,ZHANG W W,et al. Effects of Urban Landscape Pattern on Bird Community: A Case Study of Lishui District,Nanjing[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2022,38 (3): 327-333.
[35] 林鑫,王志恒,唐志尧,等.中国陆栖哺乳动物物种丰富度的地理格局及其与环境因子的关系[J].生物多样性,2009,17(6):652-663. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09065LIN X,WANG Z H,TANG Z Y,et al. Geographic Patterns and Environmental Correlates of Terrestrial Mammal Species Richness in China[J]. Biodiversity Science,2009,17 (6): 652-663. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09065
[36] 赵鸿宇.圆明园鸟类对栖息地植物生境的偏好性选择与利用研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2019.ZHAO H Y. Prefering and Usitilization of Birds for Vegetation Habitat in Yuanmingyuan[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2019.
[37]CANEDOLI C, MANENTI R, PADOA-SCHIOPPA E. Birds Biodiversity in Urban and Periurban Forests: Environmental Determinants at Local and Landscape Scales[J]. Urban Ecosystems, 2018, 21: 779-793.
[38] 赵伊琳,王成,白梓彤,等.城市化鸟类群落变化及其与城市植被的关系[J].生态学报,2021,41(2):479-489.ZHAO Y L,WANG C,BAI Z T,et al. Changes of Bird Community Under Urbanization and Its Relationship with Urbanvegetation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41 (2): 479-489.
[39] 梁宇,韦柳凤,黄玲玲,等.玉林师范学院东校区植物群落结构对校园鸟类的影响[J].湖北农业科学,2020,59(13):113-117.LIANG Y,WEI L F,HUANG L L,et al. The Influence of Plant Communities on the Birds Communities in the Eastern of Yulin Normal University[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2020,59 (13): 113-117.
[40]FERGUS C. Make a Home for Wildlife: Creating Habitat on Your Land Backyard to Many Acres[M]. Stackpole Books, 2019.
[41]SKIDDS D E,GOLET F C,PATON P W C,et al. Habitat Correlates of Reproductive Effort in Wood Frogs and Spotted Salamanders in an Urbanizing Watershed[J]. Journal of Herpetology,2007,41 (3): 439-450. doi: 10.1670/0022-1511(2007)41[439:HCOREI]2.0.CO;2
[42] 牛铜钢,赵娜,徐丹丹.京津冀平原地区近自然林营造探索[J].中国园林,2021,37(S1):145-149.NIU T G,ZHAO N,XU D D. Exploration of Near-Natural Forest Construction in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2021,37 (S1): 145-149.
[43] 林石狮,廖亮,何文,等.优良鸟类食源植物冬红Holmskioldia sanguinea的生态景观营造实践[J].广东园林,2017,39(1):71-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2641.2017.01.015LIN S S,LIAO L,HE W,et al. A Bird-Attractive Ecological Landscape with Holmskioldia sanguinea[J]. Guangdong Landscape Architecture,2017,39 (1): 71-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2641.2017.01.015
[44]HARTEL T,NEMES S,COGĂLNICEANU D,et al. The Effect Offish and Aquatic Habitat Complexity on Amphibians[J]. Hydrobiologia,2007,583 (1): 173-182. doi: 10.1007/s10750-006-0490-8
[45] 石玉帛.崇明地区无尾两栖类现状分析[D].上海: 华东师范大学, 2018.SHI Y B. Analysis on the Currentstatus of Aurans in Chongming Area[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2018.
[46]THURGATE N Y,PECHMANN J H K. Canopy Closure,Competition,and the Endangered Dusky Gopher Frog[J]. Journal of Wildlife Management,2007,71 (6): 1845-1852. doi: 10.2193/2005-586
[47] 林石狮,陈钰婷,孙延军.深圳城市公园两栖动物多样性及微栖息地构建[J].广东园林,2018,40(4):4-9.LIN S S ,CHEN Y T,SUN Y J. Diversity of Amphibian and Construction of Micro-Habitats in Shenzhen's Urban Park[J]. Guangdong Landscape Architecture,2018,40 (4): 4-9.
[48] 汪洁琼,李心蕊,王敏,等.基于水鸟栖息地保育的城市滨水生境网络构建与优化策略:以昆山市为例[J].风景园林,2021,28(6):76-81.WANG J Q,LI X R,WANG M,et al. Establishing and Optimization Strategy of Urban Waterfront Habitat Network Based on Waterfowl Habitat Conservation: A Case Study of Kunshan City[J]. Landscape Architecture,2021,28 (6): 76-81.
[49] 钟兰,苏洪林,林石狮.如何在超大城市的中心绿地营造特色生态微栖息地景观?:以深圳中心公园为例[J].广东园林,2022,44(3):7-12.ZHONG L,SU H L,LIN S S. How to Create a Landscape of Characteristic Ecological Micro-Habitats in the Central Green Spacesof Mega Cities?: Take Shenzhen Central Park as an Example[J]. Guangdong Landscape Architecture,2022,44 (3): 7-12.
[50] 杨云峰,郝晶晶,蒋梦琪.湖泊型湿地公园中两栖类动物栖息地营建研究[J].园林,2023,40(2):4-10.YANG Y F,HAO J J,JIANG M Q. Research on Restoration of Amphibian Habitat in Lake-Type Wetland Park[J]. Landscape Architecture Academic Journal,2023,40 (2): 4-10.
[51]SEBASTIÁN‐GONZÁLEZ E,GREEN A J. Habitat Use by Waterbirds in Relation to Pond Size,Water Depth,and Isolation: Lessons from a Restoration in Southern Spain[J]. Restoration Ecology,2014,22 (3): 311-318. doi: 10.1111/rec.12078
[52] 谢汉宾,张伟,李贲,等.两栖类栖息地的构建技术及效果评估[J].应用生态学报,2018,29(8):2771-2777.XIE H B,ZHANG W,LI B,et al. Construction Technology of Amphibian Habitat and the Evaluation of Its Effectiveness[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2018,29 (8): 2771-2777.
[53] 姜婧怡,张月明,高煜童.基于鸟类栖息地营建的湿地景观设计:以北戴河七里海潟湖湿地为例[J].园林,2019,36(6):56-61.JIANG J Y,ZHANG Y M,GAO Y T. Wetland Design Based on Bird Habitats Creation-Beidaihe: A Case Study of Qilihai Lagoonal Wetland[J]. Landscape Architecture Academic Journal,2019,36 (6): 56-61.
[54]MULKEEN C J,GIBSON-BRABAZON S,CARLIN C,et al. Habitat Suitability Assessment of Constructed Wetlands for the Smooth Newt (Lissotriton vulgaris [Linnaeus,1758]): A Comparison with Natural Wetlands[J]. Ecological Engineering,2017,106: 532-540. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.06.005
[55] 邬建国.景观生态学: 格局、过程、尺度与等级[M].北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007.WU J G. Landscape Ecology: Pattern, Process, Scale and Level[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007.
[56] 袁金凤.边缘效应对千岛湖陆桥岛屿植物群落结构的影响[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2011.YUAN J F. Edge Effect on Plant Community Structure on Land-Bridge Islands in the Qiandao Lake in East China[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011.
[57]SOUSA P J. Habitat Suitability Index Models: Blue-Winged Teal (Breeding)[M]. Washington, D.C.: Fish and Wildlife Service, 1985.
[58] 孙嘉徽.天津七里海湿地优先保护鸟种选择及其栖息地恢复研究[D].天津: 天津大学, 2020.SUN J H. Research on Priority Protection Bird Species Selection and Habitat Restoration in Tianjin Qilihai Wetland[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020.
[59] 王子涵.基于小型哺乳动物栖息地构建的郊野公园设计研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2021.WANG Z H. Country Park Design Based on Habitat of Small Mammals[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2021.
[60] 李佳慧,彭祚登,刘勇,等.北京市首都功能核心区国槐健康评价及其影响因素研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(1):64-73+84.LI J H,PENG Z D,LIU Y,et al. Health Evaluation and Influencing Factors of Sophora japonica in the Capital Functional Corearea of Beijing[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition),2021,49 (1): 64-73+84.
[61] 顾晓昀,徐宗学,刘麟菲,等.北京北运河河流生态系统健康评价[J].环境科学,2018,39(6):2576-2587.GU X Y,XU Z X,LIU L F,et al. Health Assessment of the Stream Ecosystem in the North Canal River Basin,Beijing,China[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39 (6): 2576-2587.
[62]BEALE C M,MONAGHAN P. Human Disturbance: People as Predation-freepredators?[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology,2004,41 (2): 335-343. doi: 10.1111/j.0021-8901.2004.00900.x
[63]TAYLOR A R,KNIGHT R L. Wildlife Responses to Recreation and Associated Visitor Perceptions[J]. Ecological Applications,2003,13 (4): 951-963. doi: 10.1890/1051-0761(2003)13[951:WRTRAA]2.0.CO;2
[64] 汪勇翔.动物友好型城市绿地系统背景下小斑块绿地生态营建探析[J].南方农业,2020,14(36):169-170.WANG Y X. Analysis on the Ecological Construction of Small Patch Green Space Under the Background of Animal-Friendly Urban Green Space System[J]. South China Agriculture,2020,14 (36): 169-170.
[65] 程秋爽.基于鸟类栖息地营造的城市边缘区绿色空间规划设计[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2020.CHENG Q S. Urban Fringe Green Space Planning and Design Based on Bird Habitats’ making[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020.
相关知识
基于水鸟栖息地营建的城市湿地公园规划设计研究
城市湿地公园的鸟类栖息地生境营造策略研究
城市湿地公园的鸟类栖息地生境营造策略研究.docx
丰富的生物多样性(下)——动物多样性
景观生态学与生物多样性保护
动物行为与保护生物多样性.pptx
城市湿地公园鸟类栖息地构建实践与方法研究
基于MAXENT模型的生物多样性生境模拟与保护优先区甄选、自然保护区布局优化评估及论文写作技巧
城市湿地公园中鸟类栖息地的营建
基于鸟类栖息地营建的湿地公园规划设计研究
网址: 生物多样性背景下城市动物生境营建的策略与方法 https://www.mcbbbk.com/newsview1203772.html
| 上一篇: 城市湿地公园的鸟类栖息地营造设计 |
下一篇: 怎么给鹦鹉做窝,打造舒适安全的栖 |
推荐分享

- 1养玉米蛇的危害 28694
- 2狗交配为什么会锁住?从狗狗生 7180
- 3我的狗老公李淑敏33——如何 6236
- 4豆柴犬为什么不建议养?可爱的 4637
- 5南京宠物粮食薄荷饼宠物食品包 4563
- 6中国境内禁养的十大鸟种,你知 4429
- 7湖南隆飞尔动物药业有限公司宠 4259
- 8自制狗狗辅食:棉花面纱犬的美 4257
- 9家养水獭多少钱一只正常 4212
- 10广州哪里卖宠物猫狗的选择性多 4122